Cladospolide B, an Antifungal Polyketide Isolated from the Fungus, Lambertella brunneola
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.59120/drj.v8i1.34Keywords:
cladospolide B antifungal, chromatography, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), structure elucidationAbstract
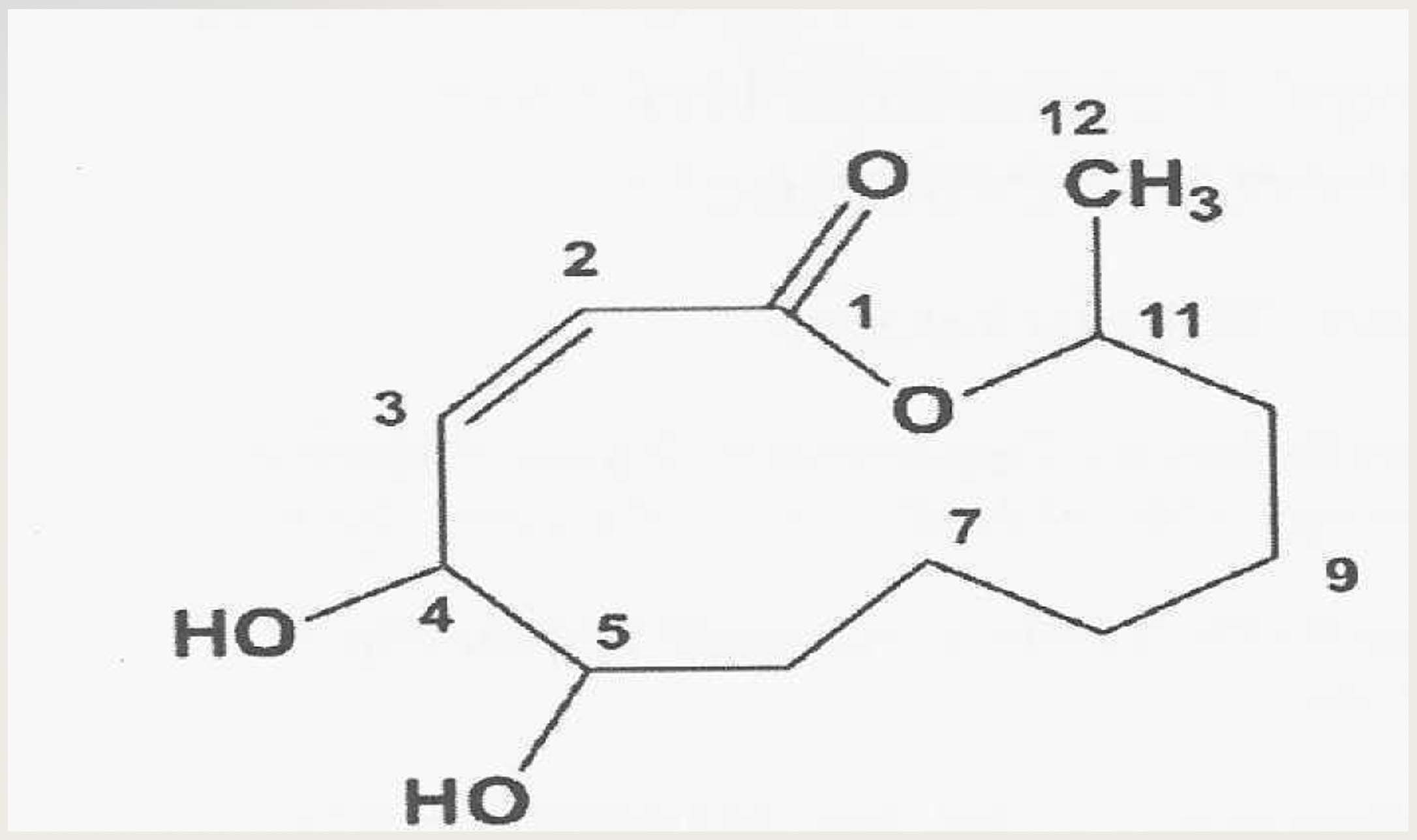
A polyketide known as cladospolide B, (Z)-4,5-dihydroxy-2-dodecen-11-olide was isolated from the culture broth of the fungus, Lambertella brunneola. The structure elucidation of this compound was based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopic data and Mass Spectroscopy (MS) analyses. Cladospolide B exhibited a seemingly weak antifungal activity and inhibited the hyphalgrowth of the phyto-pathogenicfungus, Helminthosporium oryzae(=Cochliobolus miyabeanus) by 50 % at more than 1 mg/mL but less than 5 mg/mL (1 < IC50 <5). This is the first report on the isolation of cladospolide B from L. brunneola.
Downloads
References
Fu H. (1994). Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides: Stereochemical course of two reactions catalyzed by a polyketide synthase. Biochemistry. 33 (31): 9321-9326.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2012 Wilanfranco C. Tayone, Noboru Takada

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
DRJ is an open-access journal and the article's license is CC-BY-NC. This license allows others to distribute, remix, tweak, and build on the author's work, as long as they give credit to the original work. Authors retain the copyright and grant the journal/publisher non-exclusive publishing rights with the work simultaneously licensed under a https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.









